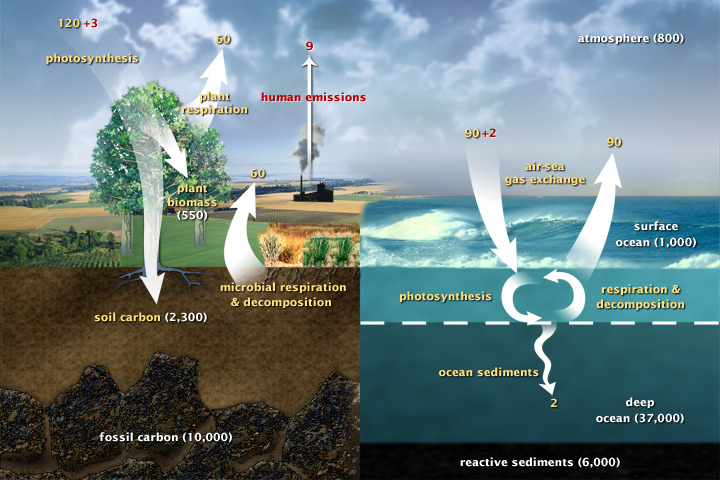
Soil organic matter (short SOM) is an important parameter when we want to store carbon in the soil. This is because most carbon is stored in the soil in this form. As you can see in the picture, more carbon is stored in the soil than there is in the atmosphere and plants combined. To learn more about this, check out this page.
Soil organic matter is also important for soil quality as it provides nutrient for plants, protects the soil from erosion by holding it better together and also increasing the water permeability. But what exactly is soil organic matter?
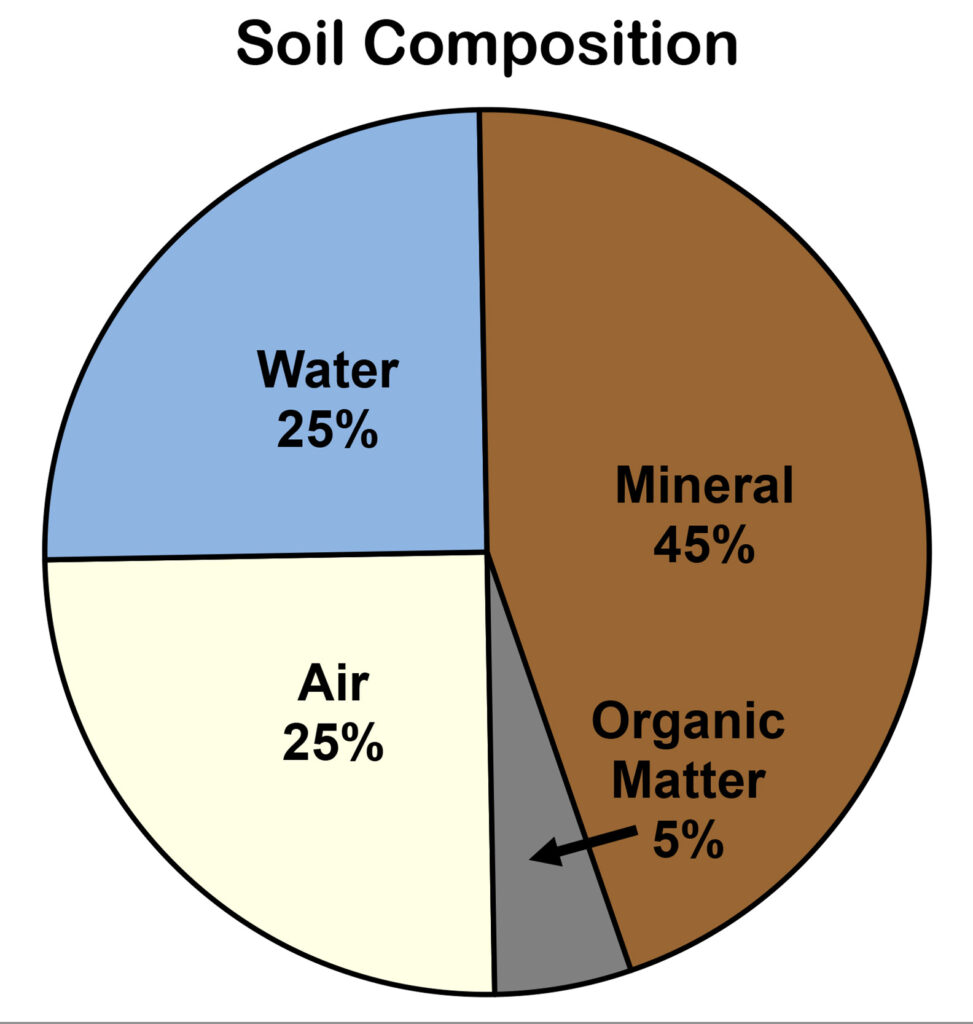
There are actually several definitions, some include living organisms as well while other don’t. I like the wikipedia definition most which says the following: “Soil organic matter (SOM) is the organic matter component of soil, consisting of plant and animal detritus at various stages of decomposition, cells and tissues of soil microbes, and substances that soil microbes synthesize.”
In general, the percentage of organic matter in the soil is said to be around 5%. However, it is important to keep in mind that soil organic matter is not a static pool, it can increase, for example when leaves are incorporated in the soil, but also decrease, for example when organic molecules are mineralised, meaning that they become inorganic and then often taken up by plants.
Image source: USDA.
